Position
- The
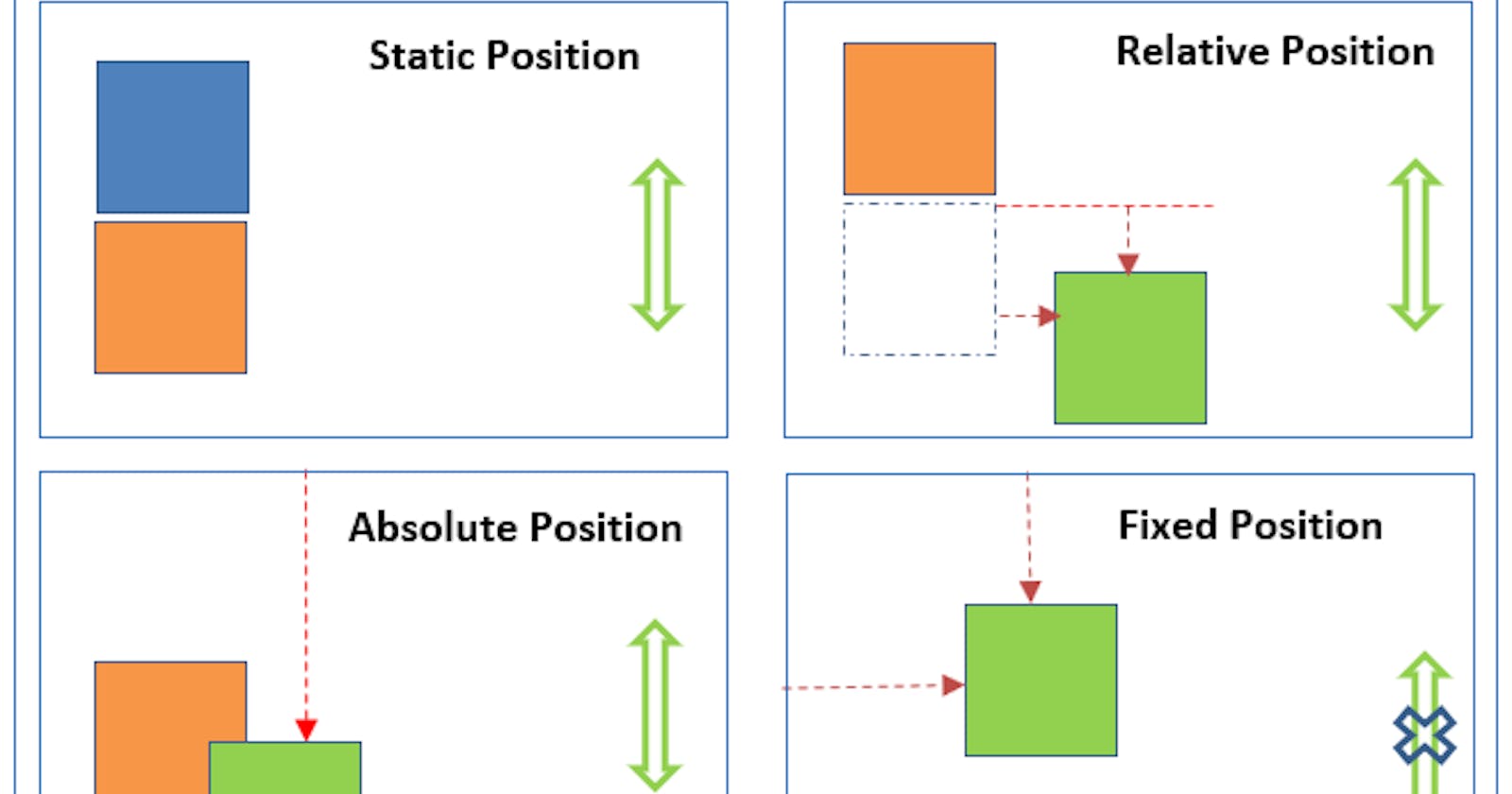
positionsets how an element is positioned in a document. Thetop,right,bottom, andleftproperties determine the final location of positioned elements. - there are mainly five types of positions in a document
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
static
- This is the default value.
- The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document. The
top,right,bottom,left, andz-indexproperties have no effect.
Syntax: position: static;
relative
- It will not affect the normal document flow.
- It looks quite similar to normal document flow. We can move/displace our element with respect to its parent element.
Syntax: position: relative;
absolute
- in absolute position element will be positioned relative to closest positionde ancestor
- It will not always visible to viewport. (not scroll with the page) It removes the element from its normal document flow.
- It displace the element with respect to the window of browser if its parent position is set to
static.
Syntax: position: absolute;
fixed
- When we use
position:fixedit will move our element out of the normal document flow. - But element will be placed according/relative to the window of browser , no matter where parent element is. It will always visible on the viewport.(scroll with the page)
Syntax: position: fixed;
stickey
- Element will act like they have
staticposition when scrolling until they hit thetop,left,right,bottomvalue. - After hitting that position it will scroll down but placing that element like
position:fixed.
Syntax: position: sticky;